
Air exits the nasal cavities via the internal nares and moves into the pharynx.
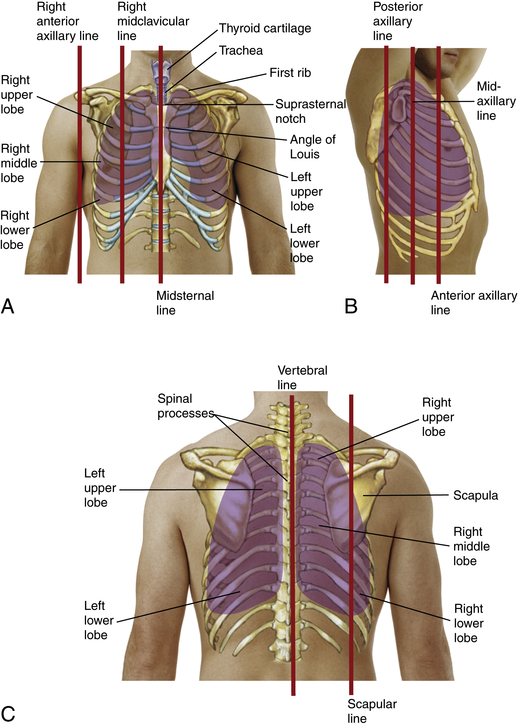
The floor of the nasal cavity is composed of the hard palate and the soft palate. The conchae and meatuses trap water during exhalation preventing dehydration. Conchae increase the surface area of the nasal cavity, disrupt the flow of air as it enters the nose, causing air to bounce along the epithelium, where it is cleaned and warmed. The nasal septum is formed anteriorly by a portion of the septal cartilage and posteriorly by the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone and the thin vomer bones.Įach lateral wall of the nasal cavity has three bony projections t he inferior conchae are separate bones and t he superior and middle conchae are portions of the ethmoid bone. The nares open into the nasal cavity, which is separated into left and right sections by the nasal septum (Figure 4.2). When discussing the nose, it is helpful to divide it into two major sections: The major entrance and exit for the respiratory system is through the nose. Watch this video:Īnatomy (Structures) of the Respiratory System The Nose and its Adjacent Structures The major respiratory structures span the nasal cavity to the diaphragm. Portions of the respiratory system are also used for non-vital functions, such as sensing odors, speech production, and for straining, such as coughing.įigure 4.1 Major Respiratory Structures. The major structures of the respiratory system function primarily to provide oxygen to body tissues for cellular respiration, remove the waste product carbon dioxide, and help to maintain acid-base balance. Although oxygen is critical for cells, it is the accumulation of carbon dioxide that primarily drives your need to breathe. A typical human cannot survive without breathing for more than three minutes, and even if you wanted to hold your breath longer, your autonomic nervous system would take control. How long you can hold your breath as you continue reading… How long can you do it? Chances are you are feeling uncomfortable already. If you hold your breath for longer than 3 minutes your autonomic nervous system will take control.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
